Good search engine rankings can benefit your online business by driving traffic and providing more chances to get conversions. SEO strategies include various ways to improve your website, like its page loading speed.
Nowadays, customers expect websites to load very quickly. Failing to fulfill this expectation may negatively affect your rankings on search engines and harm your online reputation. But what is the correlation between your site’s load speed and how well it ranks on search engine results pages (SERPs)?
In this article, we will discuss the definition of page speed, some of the best practices to improve it, and how it affects your search engine rankings.
What is Page Speed?
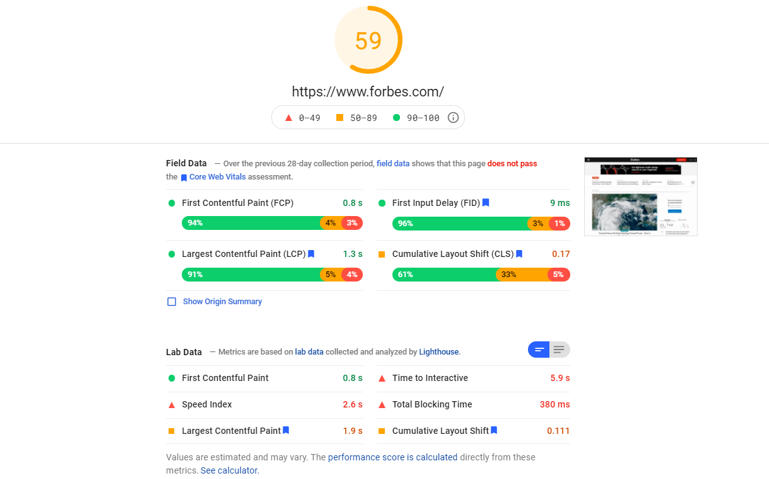 Page speed refers to the time required for a page along with all of its content to load. It is determined by several factors, including server resources, page file size, available bandwidth, and more.
Page speed refers to the time required for a page along with all of its content to load. It is determined by several factors, including server resources, page file size, available bandwidth, and more.
There are a lot of benchmarks for measuring page speed. Some of them include:
- Time before full desktop page load. This is the time required for a web page to load 100% of its content, including images and animation scripts, if there are any.
- Time to first byte (TTFB). This refers to the time required for a web browser to receive the first data packet after sending a request to a web server.
- Time to first draw (TTFD). This is the time needed for users to see any content on their screen when accessing a web page.
- First contextual paint. This is the time it takes for a web page to load enough content to allow users to read the content of that page.
Time before full desktop page load is the most straightforward way to measure your page load speed. According to Littledata, anything less than 2.3 seconds will put you in the best 10% of all benchmarked sites. Tools like Google’s PageSpeed Insights can help measure your page load speed and analyze various factors that can be improved.
Why Page Speed and SEO Rankings Matter?
Page load speed is an integral part of the user experience and it can affect your site’s performance on SERPs. Search engines like Google take it into account when ranking results. For example, a poor TTFB is one of the metrics that might lower your search engine rankings. A slow website is also more likely to have higher bounce rates, which can also negatively affect its ranking. A good position on SERPs gives your website more chances to gain clicks and organic traffic, leading to growth.
Best Practices to Improve Page Speed
Improving page load speed takes knowing how your website’s elements work is the best SEO Strategy. There are some methods and processes to do it, however. In the following sections, we’ll discuss the most effective ways to speed up your site.
Choose the Right Hosting Plan
 Your web hosting will influence your website’s performance, including its loading speed. A number of aspects, including bandwidth, server location, CMS compatibility, and extra features like a content delivery network, can affect how fast your site is.
Your web hosting will influence your website’s performance, including its loading speed. A number of aspects, including bandwidth, server location, CMS compatibility, and extra features like a content delivery network, can affect how fast your site is.
Most hosting providers offer multiple pricing plan options with different features and amounts of allocated resources. More expensive packages typically give you better bandwidth and more server locations. However, a good provider should provide a decent performance even on their cheapest plan.
Look for a web hosting that offers options that best might fit your preferences and needs. Consider if any premium features are included with the hosting plan, such as a free domain or SSL certificate. Hostinger is an example of a company offering all of the above. Lastly, make sure the service provider offers a 99.9% uptime guarantee that will allow your site to operate without interruptions.
Compress Large Files
The larger the files on your web page, the longer it will take to load them. Images and videos are examples of large files that might slow down your website. That is why compressing them is a great way to speed things up.
The best way to reduce the size of your media files is by using editing software like Adobe Photoshop or Premiere. However, if you’re not familiar with these applications, WordPress plugins can be a good alternative. Install EWWW Image Optimizer and Optimole to resize your images. Meanwhile, with tools like GIDNetwork, you can audit the quality of data compression on your site.
Minimize HTTP Requests
A web page consists of various elements such as images, stylesheets, and scripts. The web browser will make individual HTTP requests for each element when loading a page. Yahoo found that 80% of end-user response time is spent on fulfilling them. That’s why minimizing HTTP requests on your page might improve its load time. One way to figure out how many requests your site currently makes is by using your browser’s Developer Tools.
For example, if you are using Chrome, access them by right-clicking on the page and selecting Inspect. Then switch to the Network tab – it will show you the number of requests the page has made at the bottom left corner. The most effective way to reduce the number of HTTP requests on your website is to combine files. Implementing CSS sprites and image maps are a couple of the most common methods to reduce the number of image requests by combining them into a single larger file.
Leverage Browser Caching
 Browser caching refers to the process when a web browser saves some files when accessing a web page for the first time to speed up future requests. Static files such as HTML documents, stylesheets, JavaScript code, and images may be stored in a temporary directory called a cache.
Browser caching refers to the process when a web browser saves some files when accessing a web page for the first time to speed up future requests. Static files such as HTML documents, stylesheets, JavaScript code, and images may be stored in a temporary directory called a cache.
By leveraging caching, a web browser can access these files from local memory instead of downloading them from the server again. This may considerably speed up the loading process. There are two main ways to employ browser caching for your site. Advanced users may modify the .htaccess file using an FTP client like FileZilla or the file manager on their hosting control panel. Otherwise, plugins such as WP Rocket and WP Fastest Cache are a great alternative.
Use a Lightweight Theme and Fewer Plugins
The more plugins you install on your website, the longer it will take to load. This is because some plugins may use complicated code that might increase the processing duration. That’s why it might be helpful to deactivate any unnecessary plugins.
In general, ask these questions before adding a plugin to your website:
- Does it include lots of scripts, styles, or other assets?
- Does it add extra database queries to each page?
- Does it perform complex operations?
- Does it perform remote requests, like communicating with external APIs?
The same goes with your site’s theme. Avoid themes that include many animations, sliders, or functions. Besides weighing your site down, these features can make your site harder to navigate. Remember that in most cases a simpler website provides a better user experience.
Conclusion
A quick page load speed is crucial for your website’s success as it fosters a better user experience and improves search engine rankings. Additionally, search engines like Google consider how long a page takes to load when deciding its ranking on SERPs.
In this article, we have looked at five best practices to improve your page load speed and SEO, including:
- Choosing the right hosting plan
- Compressing large files
- Minimizing HTTP requests
- Leveraging browser caching
- Using a lightweight theme and fewer plugins
This article has delineated the importance of page load speed and, hopefully, helped you understand how it affects your SEO. Using the aforementioned tips, go ahead and make sure that your website’s visitors have the best browsing experience.



































